What are Climate Calculations and Climate Reporting?

Last updated: 2025-06-11
Climate calculations and climate reporting involve systematically measuring, analyzing, and communicating a company's greenhouse gas emissions and other activities related to climate change. At its core, it is about understanding and documenting how a company impacts the environment, both through direct and indirect emissions, to take action to reduce this impact. Climate reporting has become an increasingly important tool for both complying with international regulations and meeting growing demands from customers, investors, and other stakeholders who require sustainability efforts. The first step in the reporting process is to start with climate calculations.
As of 2024, the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) has come into effect, meaning that more companies than before must report their climate impact. For businesses with a turnover exceeding 40 million euros or more than 250 employees, it is now mandatory to report emissions and sustainability data, making climate calculations and reporting an integral part of annual financial reports. For smaller companies that may not be directly affected by these requirements, there is still increasing pressure to adapt, calculate, and report their climate impact to remain competitive and meet the sustainability expectations of their partners and customers.
Another key driver for engaging in climate reporting is that it strengthens a company’s credibility and brand. As awareness of the climate crisis grows, both customers and investors are increasingly looking for companies with a clear and transparent sustainability strategy. By being proactive and demonstrating a commitment to reducing emissions, companies can create competitive advantages.

Why is climate reporting important?
There are several strong reasons for companies to begin climate reporting, both from a regulatory perspective and from a business and competitive standpoint:
Regulations and legal requirements
As mentioned, the EU has introduced new directives making climate reporting mandatory for a large share of businesses. This means that companies must disclose their greenhouse gas emissions and other climate-related factors in accordance with international standards, such as the Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHG). For organizations not yet covered by these directives, climate reporting presents an opportunity to prepare for future regulatory changes.
Competitive advantage
Companies that report their climate impact and implement sustainable practices often gain a stronger position among customers, investors, and potential business partners. In an increasingly sustainability-conscious market, transparency and responsible business practices are becoming more important. Demonstrating a serious sustainability strategy can be key to winning contracts or attracting new investors.
Investor requirements
Investors and financial institutions are placing greater emphasis on sustainability and climate impact when making investment decisions. Companies that cannot demonstrate a plan for reducing emissions and managing climate risks may find it harder to secure funding.

What is CSRD?
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) is an EU directive requiring companies to report their sustainability impact in a more standardized and detailed manner. The purpose of CSRD is to improve transparency in how businesses manage environmental impact, social responsibility, and other sustainability-related aspects.
From 2024 onward, CSRD applies to a much larger group of companies than before. Previously, sustainability reporting was required only for large corporations, but now the requirements extend to include more companies, including publicly listed firms that were not previously obligated to report.
The new regulations require companies to use the EU’s sustainability reporting standards (ESRS), ensuring stricter monitoring of how businesses disclose their environmental impact, including climate emission calculations. Companies must also report on the risks and opportunities that climate change presents for their operations.
Another crucial aspect is that companies must include their entire value chain in their reporting. This means that suppliers and subcontractors must also be accounted for in climate reporting. As a result, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that are part of larger companies' supply chains may be indirectly affected by CSRD requirements.

VSME and Omnibus
VSME (Voluntary Sustainability Reporting Standard for SMEs) and Omnibus are two initiatives related to CSRD, aiming to facilitate sustainability reporting for small and medium-sized enterprises. The goal of these changes is to make sustainability reporting more manageable and less resource-intensive for SMEs while continuing to drive corporate sustainability efforts forward.
Omnibus and its impact on small and medium-sized enterprises
The Omnibus proposal aims to reduce the administrative burden on smaller businesses required to comply with CSRD regulations. One of the biggest changes is raising the threshold for which companies are subject to CSRD reporting requirements, meaning fewer SMEs will be directly affected by these extensive reporting obligations. This makes the process more manageable and less costly for smaller firms.
Additionally, Omnibus introduces protections for SMEs within the supply chain. In practice, this means that large companies can no longer impose stricter sustainability requirements on their smaller suppliers than those outlined in the simplified VSME standard. However, the EU's target of net-zero emissions by 2050 remains in place, and even smaller companies should calculate their climate footprint to prepare for future customer and EU demands.

VSME – A voluntary sustainability standard for small businesses
VSME (Voluntary Sustainability Reporting Standard for SMEs) is a voluntary standard for small and medium-sized enterprises that are not subject to CSRD’s comprehensive reporting requirements. VSME is designed to allow SMEs to report their sustainability efforts in a structured but less resource-intensive manner than full CSRD compliance. The standard aims to provide small businesses with a simple and manageable way to communicate their sustainability initiatives without unnecessary administrative burdens.
Companies following VSME can still demonstrate to customers, investors, and other stakeholders that they are committed to sustainability, without having to produce the extensive and detailed reports required of larger firms. This makes VSME an important tool for small businesses seeking transparency in their sustainability efforts while keeping costs and administrative efforts low.

Steps for small and medium-sized enterprises to prepare
Even though Omnibus and VSME reduce the most extensive requirements for SMEs compared to larger companies, they will still be indirectly affected through their business relationships. Since larger companies subject to CSRD must report their climate impact throughout their entire value chain, they will place demands on their suppliers—meaning SMEs may need to adapt to remain competitive.
To prepare for future changes, small and medium-sized enterprises should consider taking the following steps:
1. Understand the new requirements
By understanding what CSRD and VSME entail, even if the company is not directly affected, businesses can better prepare for potential demands from customers and investors.
2. Map sustainability data
Prepare by collecting and structuring sustainability information, including climate calculations that clearly show data on CO₂ emissions, energy and resource consumption, as well as working conditions and gender equality.
3. Establish internal routines
Implementing simple systems to track and document sustainability data will help businesses prepare for future requirements.
4. Collaborate with larger companies
Since large companies must report their impact across the value chain, it is crucial for small businesses to proactively work with their key customers to understand their sustainability needs.
5. Educate employees
A basic understanding of sustainability reporting within the organization will make adaptation easier as requirements evolve.

Summary
Climate reporting is a vital part of future business strategy, and it is becoming increasingly important for companies to start reporting their emissions and sustainability efforts. For small and medium-sized enterprises, CSRD, Omnibus, and VSME present both challenges and opportunities. By understanding the new regulations and taking proactive steps to gather and report sustainability data, businesses can position themselves competitively in an increasingly sustainability-conscious market.
For companies that want to remain relevant and maintain business relationships, sustainability reporting is not just an administrative task—it is a strategic advantage. By utilizing tools like VSME, small and medium-sized enterprises can ensure they conduct sustainability work in a way that is both efficient and scalable for their operations.
Automated climate calculations with GoClimate
GoClimate automatically calculates your company’s climate emissions based on invoices and receipts. The platform provides an efficient and professional way to manage sustainability efforts without being time-consuming or costly. Emission calculations follow the GHG Protocol and can be easily applied to both CSRD and VSME reports.
By linking your accounting system to GoClimate, you get an overview of your company’s total emissions and can also see which suppliers contribute the most to your emissions. The platform helps you set automatic goals according to SBTi and track progress month by month. With Scope overviews, industry comparisons, and concrete action suggestions, you get a clear plan to reduce emissions.
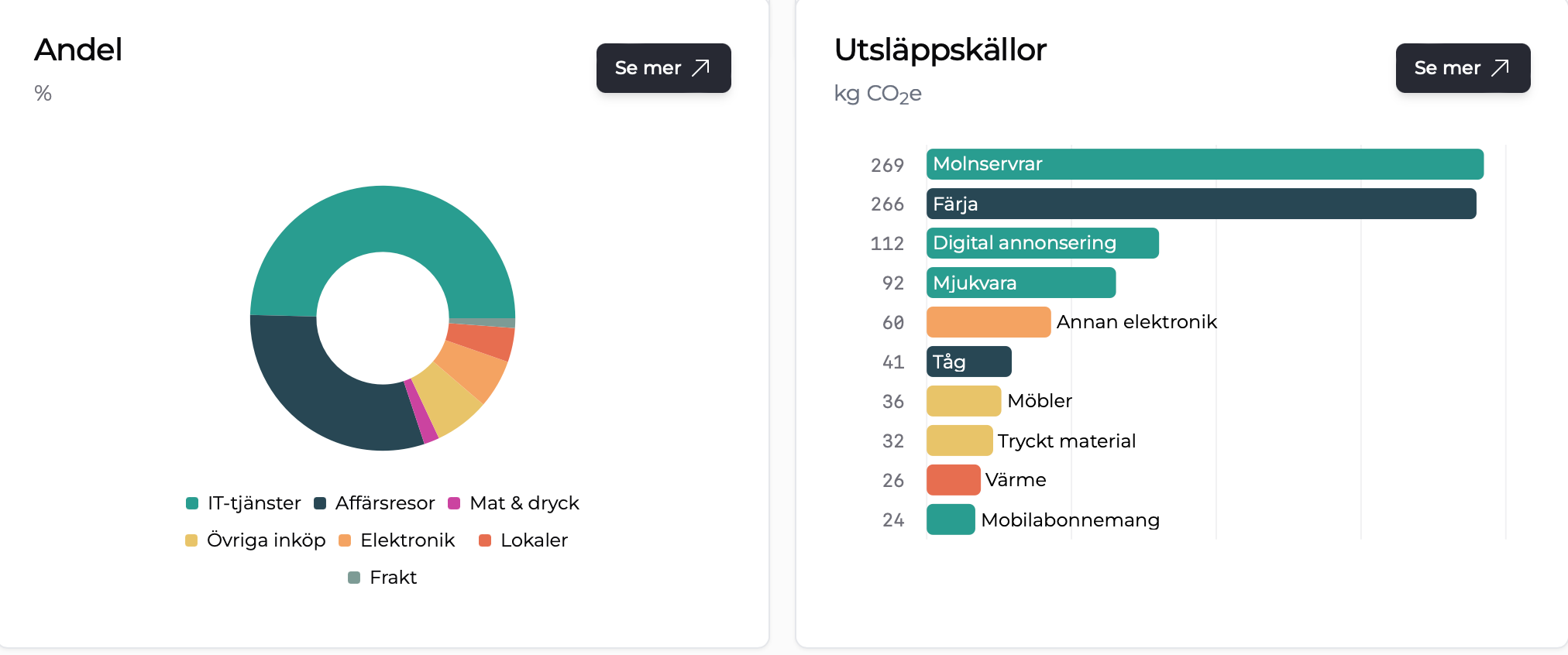
GoClimate’s automatic climate calculations are carried out according to the GHG Protocol and are based on data from the accounting system.
Learn more about the platform here or contact us for more information or any questions!
Related content
Here you can find articles and pages relevant to this subject.