This is part three of our article series about how we consider the climate projects we support. This part is about the projects that contribute to reduced emissions and covers the projects that GoClimate primarily supports today.
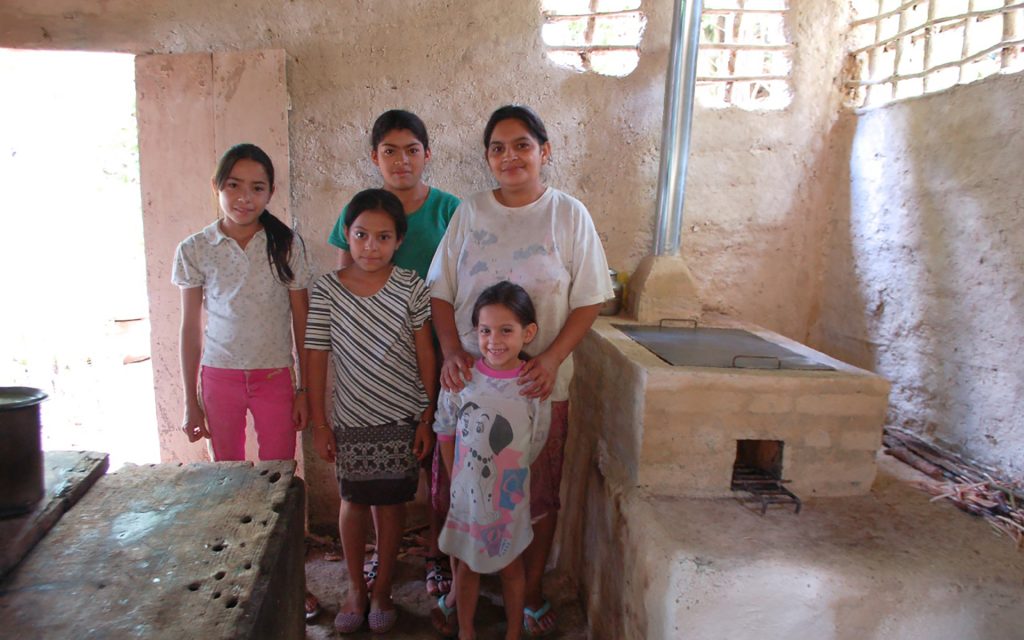
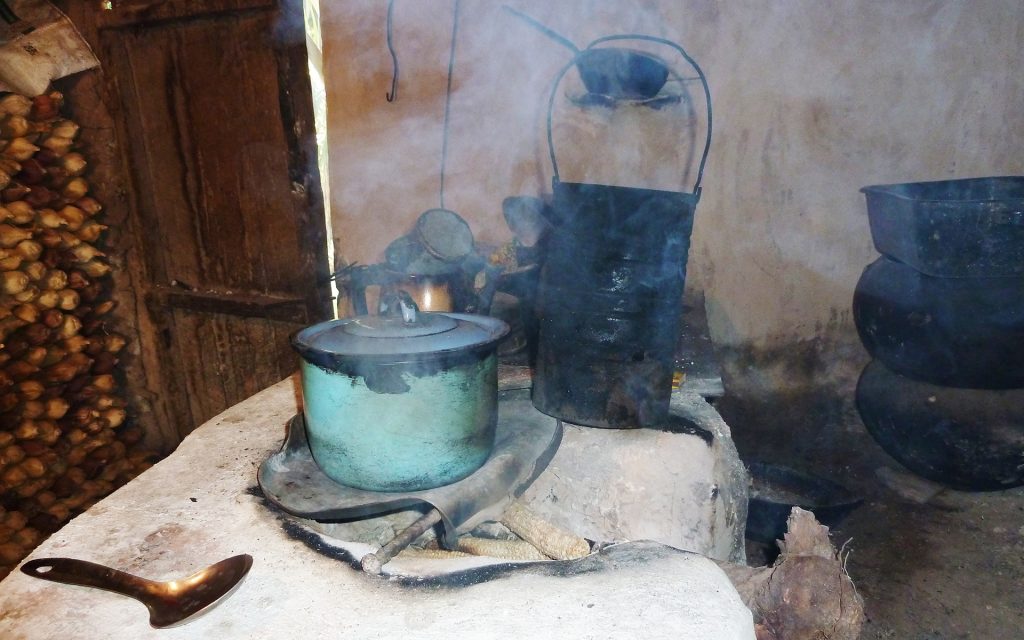
This category includes, for example, energy-efficient stoves that reduce the need for wood and thus deforestation. There are also projects in renewable energy that reduce the need for coal power plants and those that handle harmful methane gas by converting it into electricity, replacing fossil energy sources. More examples of these climate projects are available here.
2.1 Why We Support This Type of Project
There is scientific consensus that it is urgent to reduce the world’s emissions. Therefore, it is reasonable that at the present time, when there is so much left to do, the focus should simply be on supporting projects that reduce the world’s emissions.
2.1.1 The Technology is Already Here
To reduce emissions, both capital and technology dissemination are required. The necessary technology to cope with climate change already exists to a large extent, but it needs to be spread, financed, and implemented. The type of climate financing that we, our members, and customers contribute to plays a big role here; this is exactly what is needed to speed up the transition. But it’s not just a question of investing money, the projects must be effective and well thought out too.
2.2 Challenges with These Types of Projects
The climate benefit of the projects is often calculated based on hypothetical scenarios, which can be problematic. Changed subsidies, norms, and knowledge levels can affect the projects over time. Some projects may no longer need support due to technical development and price reductions in renewable energy. However, the role of climate financing is crucial. It has historically contributed to economies of scale and price reductions, meaning that some projects no longer need the same support. To manage these dynamic factors, one can choose to support newer projects or specific years.
Despite the complexity of these projects, we are convinced that they can be supported effectively, especially if the right type of project is chosen.
2.3 Projects We Do Not Support in This Category
In this category are projects that we consider to be less efficient or problematic. For example, we do not support the construction of large-scale hydroelectric power plants, as they require large land areas and can have a negative impact on both the environment and local communities.
New renewable energy projects in countries not on the UN’s list of least developed countries are also not certified according to the standard – Gold Standard – that we go by. These projects are often considered to not need financial support to the same extent as they did in the past.
However, it is important to understand the climate credit market and how it affects the lifespan and financing of projects. We still support certain energy projects that would not be certified today, because if we stop supporting certain projects that were certified because climate financing was deemed necessary earlier, it could undermine the confidence in the climate credit market and make it more difficult for future projects to get financing.
We also do not support local projects in Sweden, as the country already has access to financing and relatively low climate emissions compared to other regions. Our strategy is to support projects where they can have the greatest positive climate impact. Even though projects like solar cell support in Sweden can be beneficial, financing does more good when used in other countries, for example, those with a higher mix of fossil fuel sources in their electricity mix.
Please get in touch ([email protected]) if you think there’s anything we’ve missed; we are always open to learning more!